Hitting the inbox is paramount, no matter how big or small a sender you are.
If not…
- Your marketing campaigns go unseen.
- Your transactional emails fail to reach their destination.
- Your efforts translate into lost revenue and damaged sender reputation.
At Mailtrap, we help you improve deliverability with your organically built audience, whether it’s for marketing campaigns or critical transactional communications.
This comprehensive guide walks you through the essential strategies and best practices that high-volume senders use to achieve optimal inbox placement and maximize their email ROI.
If you’re a business grappling with these challenges, consider a deeper dive with our experts. ⬇️
How to improve email deliverability: a snapshot
Achieving high email deliverability is an ongoing process that requires a strategic approach across technical setup, sender reputation, list management, and content optimization.
Here’s a quick overview of the quick wins we’ll explore in detail:
| Action | Why it’s a Quick Win & Its Impact |
| Implement DMARC with p=none | Set up DMARC, even just for a monitoring-only policy (p=none)]. It builds on SPF and DKIM (which verify who sent the email and if it was changed) by providing reports that show you exactly who is sending email on behalf of your domain. [Improve technical setup] |
| Add the list-unsubscribe header | The header adds a direct “unsubscribe” button within the email client (like Gmail or Outlook), making it easy for recipients to opt out. This is also required by major mailbox providers (Google, Yahoo, Outlook) [Improve technical setup] |
| Automate hard bounce removal | Ensure your email platform (ESP/MTA) automatically removes these addresses immediately to protect your sending health. [Improve email list management] |
| Monitor ip/domain blacklist status | Proactively check if your sending IP address or domain name appears on these lists. If you’re listed, it means ISPs might block your emails. Early detection helps you quickly find out why you’re listed and start the process of getting removed. [Improve sender reputation] |
| Prioritize double opt-in (DOI) | The extra step ensures the recipients genuinely want your emails and that their address is valid. It leads to a much cleaner, more engaged list, significantly reducing future spam complaints and bounces. [Improve email list management] |
| Subscribe to mailbox provider FBLs | Sign up for tools like Google Postmaster Tools and Microsoft SNDS to get direct FBL reports. This feedback is invaluable for quickly identifying and removing those who complain. |
| Segment by engagement & implement a sunset policy | Stop sending to people who consistently don’t open or click your emails. Focusing your sends on active subscribers boosts positive engagement signals for the ISPs. Implement a “sunset policy” to gradually reduce or stop campaigns for inactive users. [Improve email list management] |
| Optimize subject lines & preheaders | Craft clear, concise, relevant, and compelling lines. Avoid “spammy” triggers (like excessive ALL CAPS, too many exclamation marks, or phrases that sound like scams). A good subject line and preheader directly lead to higher open rates. [Improve email content] |
Email deliverability improvement strategies
Achieving consistent inbox placement for your high-volume sends demands a multi-faceted approach.
- Email infrastructure setup
- Sender reputation
- email list quality
- email sending
- email content quality
- email user engagement
I will break down each aspect into an actionable how-to. Let’s start with the technical improvements.
Improve email infrastructure
To improve email infrastructure, you need to focus on email authentication, domain configuration, and email security.
It will show Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and mailbox providers that your emails are legitimate and secure. And actually, all major ISPs require authentication protocols if you’re to be considered a legitimate sender ➡️(Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo, and Apple Mail).
I’ll explain what you should check in your current setup, why this matters, and what steps you need to take to improve your inboxing rates.
Email authentication protocols
Double-check the protocols’ setup and fix the following if you identify any issues.
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework): Check your SPF record with Mailtrap’s Free SPF Record Checker. If an email originates from a server not listed in your SPF record, it’s likely to be flagged as suspicious or spam.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): Utilize Mailtrap’s Free DKIM Record Checker to validate your setup.
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) builds on SPF and DKIM. For large senders, it helps gain visibility into spoofing attempts. Use our Free DMARC Record Checker to ensure that DMARC is correctly configured.
- BIMI (Brand Indicators for Message Identification): Display your brand’s logo next to your authenticated emails in the recipient’s inbox. While not directly a deliverability protocol, BIMI enhances brand recognition and user trust, indirectly boosting engagement.
For a deeper dive into authentication, refer to our guide on Email Authentication Explained: SPF, DKIM, DMARC, BIMI.
DNS records for email sending
Proper DNS configuration ensures your email servers are correctly identified and email can be routed effectively. So, here’s your homework 😀
- rDNS (Reverse DNS or PTR records): Maps an IP address back to a domain name, acting as a “reverse lookup.” ISPs often check PTR records to ensure the sending IP is legitimate and not a generic or dynamic address, which helps prevent spam.
- MX records (Mail Exchange records): Specify the email servers responsible for accepting email messages on behalf of your domain. Okay, these are primarily for inbound email, but correctly configured MX records indicate a professionally managed domain, lending credibility to your outbound emails.
Custom domain configurations
Use custom configurations instead of the generic ones provided by your Email Service Provider. Here are the customizations to make.
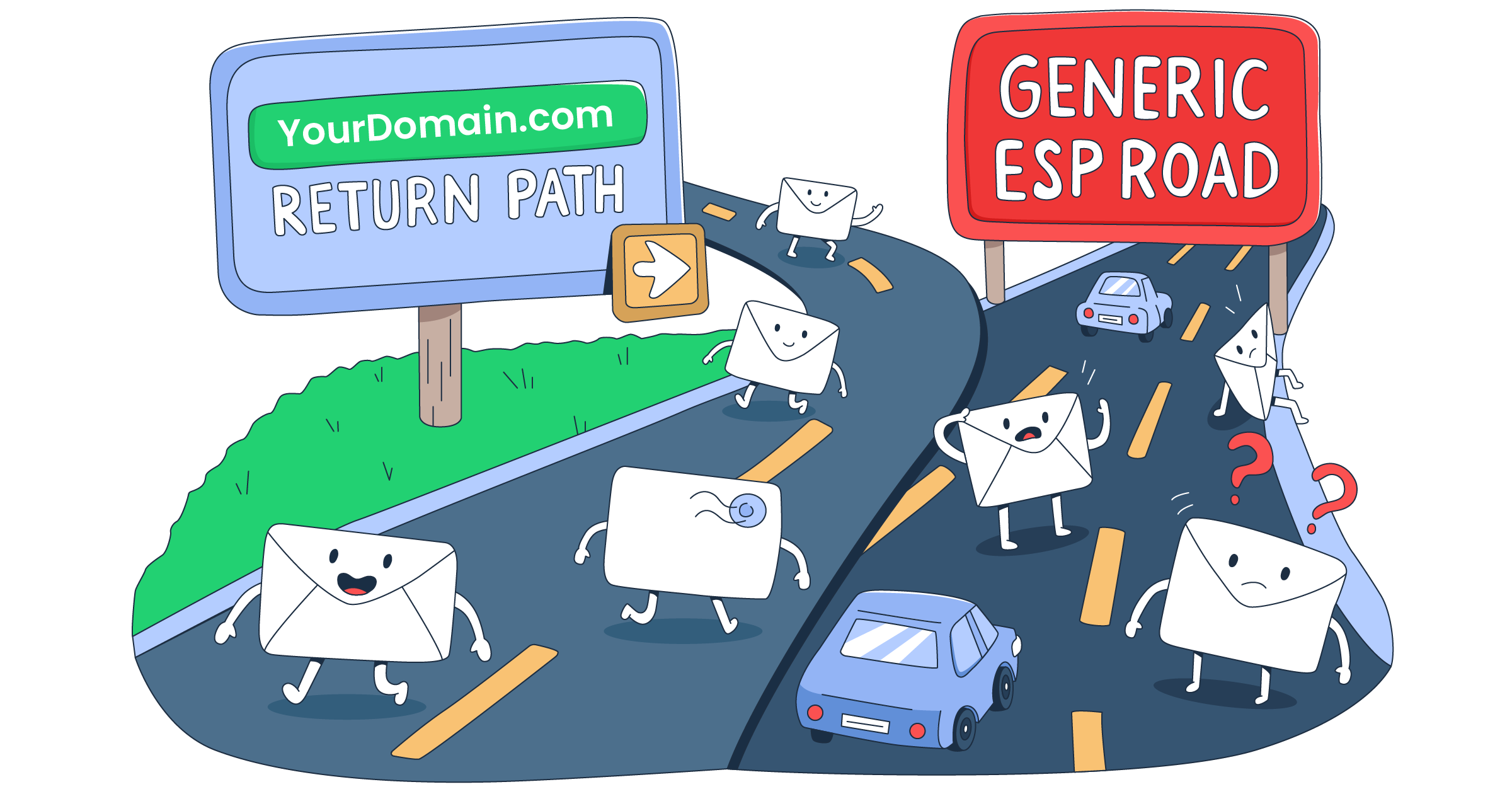
- Custom return path (MAIL FROM): Use a custom subdomain (e.g., bounces.yourdomain.com) for your return path to ensure that bounce handling doesn’t negatively impact your main sending domain’s reputation and allows for easier tracking.
- Custom tracking URLs: If your ESP uses tracking links (for opens, clicks), ensure these are branded with your domain (e.g., clicks.yourdomain.com). This avoids sharing reputation with your ESP’s generic tracking domain and instills greater trust in recipients and filters.
Email transmission security standards
Secure emails in transition to protect sensitive data and signal trustworthiness to mailbox providers. This is what to do 🔽
- TLS (Transport Layer Security) / STARTTLS: Most ISPs require and prefer TLS connections. You should always enforce STARTTLS where possible.
- MTA-STS (Mail Transfer Agent Strict Transport Security): A security standard that forces email servers to use TLS when sending email. It helps prevent downgrade attacks where an attacker might force a connection to use unencrypted channels. Mailtrap’s blog has an in-depth guide on the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) Explained.
- TLS-RPT (TLS Reporting): Companion to MTA-STS, TLS-RPT allows you to receive reports on TLS connection issues, providing visibility into potential security problems that could affect deliverability.
Further reading: STARTTLS vs SSL vs TLS Explained
Mailbox provider Feedback Loop (FBL)
Subscribe to FBLs (e.g., through Google Postmaster Tools or Microsoft SNDS) to quickly identify and remove complainers from your list. Of course, this prevents further complaints that damage your reputation.
For more details on the feedback loop, check: What Is Email Feedback Loop and Why Is It Important?
Email Headers
Properly configured email headers provide necessary information for email servers and can influence how your emails are processed and delivered.
- Message ID: Most times, it’s automatically generated. However, ensure it’s correctly formatted and present to help with email tracking and debugging.
- Date header: Accuracy here is important for chronological sorting and filter evaluation. So, check these headers particularly if you operate in different time zones.
- List-unsubscribe header: Make sure this header provides a one-click unsubscribe option directly within the email client interface. New sender requirements mandate it, and it genuinely helps with spam complaints. Learn more about its importance: List Unsubscribe Header: Why and How to Use.
- Precedence header: Used to indicate the nature of an email (e.g., precedence: bulk or precedence: junk) to inform receiving servers that it’s a bulk email and should not generate auto-replies. While less common now, it can still have an impact.
Use a reliable email service provider
If you handle transactional and marketing campaigns at a volume, a reliable Email Service Provider (ESP) is essential. Check whether the ESP provides the necessary technical infrastructure to ensure your emails consistently reach recipients’ inboxes.
For instance, Mailtrap Email API/SMTP offers a robust infrastructure designed for high-volume senders. We focus on maximum throughput and optimal inbox placement by leveraging the following:
- Automatic email authentication: Mailtrap configures and manages essential authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC). This process verifies your emails as legitimate, significantly reducing the likelihood of them being flagged as spam or rejected by receiving servers.
- Dedicated sending streams: Mailtrap provides separate, isolated sending streams for different email types (e.g., transactional vs. marketing). This prevents potential deliverability issues from spilling from one email type to another (marketing to transactional and vice versa).
- Robust security and compliance: We are compliant with regulations such as ISO 27001 and GDPR, ensuring your data and your recipients’ privacy are protected.
All in all, we aim to take the headache out of email deliverability. Let Mailtrap simplify your email infrastructure so the emails land where they belong 🔽
Improve sender reputation
Your sender reputation encompasses your IP reputation and domain reputation. It’s a critical factor ISPs use to determine whether your emails reach the inbox or are sent to the spam folder. Check the key aspects you need to consider.
IP reputation management
The reputation of the email-sending IP address (or addresses) directly impacts your deliverability. Here’s what to keep in mind.
- Shared vs. dedicated IP:
- Shared IP address: When choosing an ESP, make sure they adhere to the security protocols and have internal mechanisms to weed out spammers. Ideally, like Mailtrap, the provider should offer separate sending streams for different types of messages.
- Dedicated IP address: If you send more than 100K emails a month, I’d encourage you to choose a dedicated IP address. It gives you complete control over the IP reputation and allows for more precise IP warming. You can check more on the topic: Shared vs Dedicated IP in Email Sending.
- IP warming & re-warming: When you get a new dedicated IP or significantly change your sending practices (like introducing a new domain, subdomain, or a third-party service for cold emails), you must gradually increase your sending volume. This is the IP warm-up, building trust with ISPs over time. Re-warming is necessary if you have periods of inactivity or significant changes in volume.
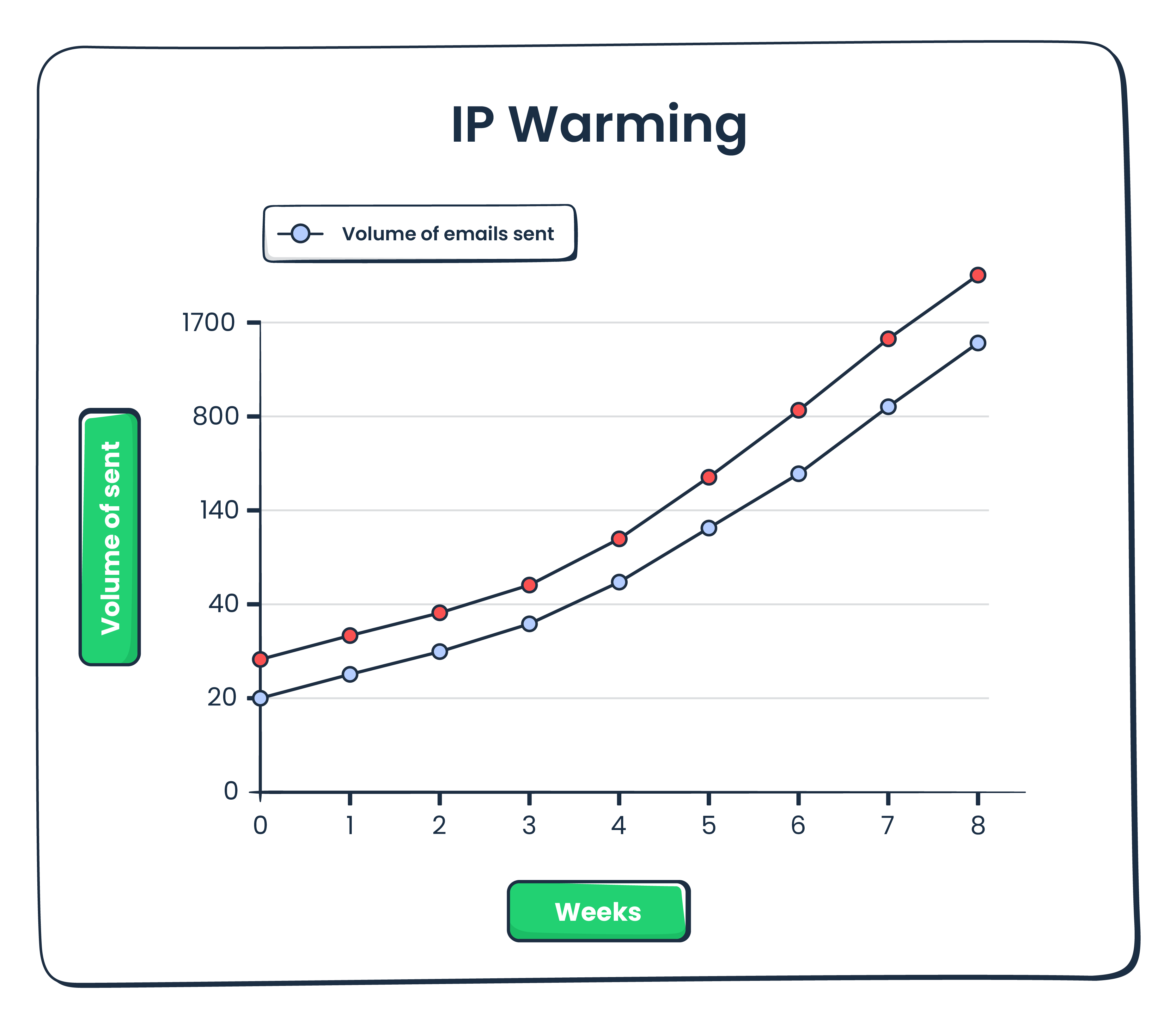
- IP pooling strategies: If you send at high volumes (e.g., 1M+ emails a month) or have diverse email streams, use multiple dedicated IPs grouped into “IP pools.” This strategy allows you to distribute the sending load and isolate different types of email (e.g., transactional vs. marketing) to separate IPs, protecting the reputation of critical streams.
- IP segmentation by email stream (Reminder): Send different types of emails (e.g., transactional, marketing, notifications) from separate dedicated IPs or subdomains to isolate their reputations. If your marketing emails encounter issues, your critical transactional emails remain unaffected.
- IP blocklist monitoring: Regularly check if your sending IPs have been listed on any public or private blocklists. ISPs use these lists to identify and block email from suspicious sources. You can use Mailtrap’s Free IP Blacklist Checker to monitor your IP status.
- IP delisting process: If your IP gets blocklisted, promptly follow the delisting procedures of the specific blocklist provider. This typically involves identifying and rectifying the root cause of the listing (e.g., spam complaints, spam traps) and then requesting removal.
Email domain reputation management
Similar to your IP, the reputation of your sending domain is crucial because it represents your brand’s trustworthiness, which is often expressed through a sender score.
- Domain warming techniques: As a reminder, new sending domains or subdomains benefit from a gradual increase in sending volume, especially to highly engaged recipients.
- Subdomain strategy for isolation: Using distinct subdomains for different email streams (e.g., marketing.yourdomain.com, transactional.yourdomain.com, newsletter.yourdomain.com) allows you to compartmentalize reputation. If marketing.yourdomain.com faces email performance issues, transactional.yourdomain.com remains unaffected.
- Google Postmaster Tools insights: This free tool from Google provides valuable data on:
- Your sending domain’s reputation
- IP reputation
- Spam rate
- Authentication and delivery errors for Gmail recipients.
Regularly monitoring these insights is critical for proactive reputation management.
- Microsoft SNDS data usage: Microsoft’s Smart Network Data Services (SNDS) provides similar insights for Outlook.com and other Microsoft properties. It offers data on spam complaints, filtered emails, and overall reputation, helping you troubleshoot deliverability issues specific to Microsoft inboxes.
- Consistent domain branding: Ensure your “From” address, custom tracking domains, and custom return-path domains all consistently use your primary sending domain or closely related subdomains. This consistency builds brand recognition and trust. You can also use Mailtrap’s Free Domain Blacklist Checker to monitor your domain’s status.
Recipient engagement impact on reputation
Recipient engagement is a powerful signal to ISPs about the quality and relevance of your emails. High positive engagement boosts your reputation, while negative email engagement can quickly degrade it.
- Positive engagement signals: Keep an eye on opens, clicks on links within the email, replies, marking an email as “not spam,” and adding your “From” address to their address book. ISPs interpret these actions as signs that recipients value your emails.
- Negative engagement signals: The most damaging are spam complaints. Other negative signals include deleting emails without opening them, unsubscribing, and emails bouncing back as undeliverable.
- Engagement-based segmentation: Segment your email list based on engagement levels (e.g., highly engaged, moderately engaged, inactive). Send your most valuable content to your most engaged segments to reinforce positive reputation signals. Also, create reengagement campaigns to motivate other, less-engaged segments.
- Effective sunset policies: Implement policies to gradually reduce or stop sending to consistently unengaged subscribers. Sending to inactive users generates low engagement and can accumulate negative signals over time, harming your overall deliverability, particularly if you send a large volume of emails.
Reputation recovery strategies
If your sender reputation takes a hit, a systematic approach is needed for recovery. So, don’t panic, but do the following.
- Diagnose root cause of damage: Identify why your reputation suffered. Was it a sudden spike in spam complaints, high bounce rates, or a blocklisting? Utilize tools like Google Postmaster Tools, SNDS, and DMARC reports to pinpoint the issue.
- Create a step-by-step recovery plan: This might involve pausing sends, removing problematic subscribers, re-engaging cautiously, or appealing blocklist entries.
- Communication with ISPs/blocklist owners: In some cases, direct communication with the relevant ISP postmaster teams or blocklist operators may be necessary after you’ve addressed the underlying issues. Be prepared to explain the steps you’ve taken to resolve the problem.
- Gradual re-warm and ramp up the volume: Reestablish your sending reputation slowly after addressing the root cause. Begin with highly engaged segments and gradually increase volume, monitoring email deliverability rate closely. This is similar to the initial IP warming process, but with an added focus on demonstrating sustained good behavior.
Improve email list management
Your email list is your most valuable asset in email marketing. Maintaining its quality and relevance is essential for consistently good email deliverability. Here, I will explain what you should do to improve the quality of your email list and why you should do it.
Optimize list acquisition methods
The journey to high deliverability begins the moment you acquire a subscriber, where quality over quantity is the golden rule. So, when a new subscriber comes knocking on your door, focus on the following.
- Permission-based opt-ins: Always ensure you have explicit permission from every subscriber. This means they’ve actively agreed to receive emails from you. Avoid any pre-checked boxes.
- Clear consent mechanisms (GDPR focus): The opt-in forms must clearly state what the subscriber is signing up for, how often they’ll hear from you (e.i, the number of emails per week/month), and what kind of content to expect. For users in regions with strict data protection laws like GDPR, ensure consent is freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous. (To stress, it’s a legal requirement, not a nice-have 😀)
- Transparent data usage statements: Clearly communicate your privacy policy and how subscriber data will be used (data security at rest and in transit). This builds trust and sets expectations, reducing the likelihood of spam complaints later.
- Source quality validation: Implement processes to monitor and validate the source of your new subscribers. This helps identify and eliminate any channels that might inadvertently bring in low-quality or non-consenting leads.
- Avoiding purchased or rented lists: Never! Lemme say that again, NEVER 😀, under any circumstances, purchase or rent email lists. These lists are notorious for containing spam traps, inactive addresses, and non-consenting users, leading to immediate and severe damage to your sender reputation and deliverability.
Implement effective opt-in processes
The method you use to onboard new subscribers directly affects the quality and engagement of your list. Therefore, I’d like to dissect opt-ins further to give you an actionable framework you can apply right away.
- Single opt-in (SOI) vs. double opt-in (DOI) strategies:
- Single opt-in (SOI): Subscribers are added to your list immediately after filling out a form. While quicker for the user, it carries a higher risk of invalid addresses or accidental sign-ups.
- Double opt-in (DOI): Subscribers receive a confirmation email that they must click to verify their subscription. This is the gold standard for high-volume senders, as it guarantees consent, confirms email validity, and leads to significantly higher engagement and deliverability rates.
- DOI confirmation email design and timing: Your DOI email should be clear, concise, and sent immediately after sign-up. Its design should be simple, with a prominent call-to-action to confirm the subscription. It’s a transactional email, actually.
- Managing and storing consent records: Maintain auditable records of when and how each subscriber provided consent. This is crucial for compliance with data protection regulations and for demonstrating legitimacy to ISPs if questioned. When preparing compliance documentation for audits or internal reviews, teams often need to combine PDF files into a single report to streamline consent record-keeping and sharing.
- Welcome email for new subscribers: Send a timely welcome email to new subscribers. This reinforces their decision, sets expectations, and provides initial value, kickstarting positive engagement.
Advanced list hygiene techniques
Proactive list cleaning is vital to prevent bounces, reduce spam complaints, and protect your sender reputation from degradation.
So, buckle up and employ the following email deliverability best practices:
- Automate hard bounce removal rules: Implement automated systems to remove hard-bounced email addresses from your list immediately. Hard bounces indicate permanent delivery failures and negatively impact your reputation. For more on this, see Email Bounce Explained: Definition, Reasons, Best Practices
- Monitor soft bounces and establish retry logic: Monitor soft bounces (temporary delivery issues) and implement a retry strategy (e.g., a couple of retries in an hour or two after the initial bounce). If an address soft bounces repeatedly, consider temporarily suppressing or removing it after a defined number of failures. Check out our blog post to learn more about the Difference Between Hard and Soft Bounce.
- Detect and mitigate spam traps proactively: Spam traps are invalid email addresses used by ISPs to identify spammers. Hitting them severely damages your reputation. Regularly clean your list and scrutinize acquisition sources to avoid them. For more details, read ➡️ What is a Spam Trap: Guide for Email Marketers and Software Developers.
- Using list validation and cleaning services: Consider using third-party email list validation and cleaning services for large lists. Better yet, if you got programming skills or have a dev team to back you, consider baking an API validation and sanitization into your lead-capture backend. Whichever way, these tools can identify invalid, risky, or low-quality email addresses before you send to them. Read our expert tips on Email List Cleaning: Best Practices from an Expert.
Strategic list segmentation for relevance
Segmentation improves deliverability by ensuring your emails are relevant to your audience, leading to higher engagement.
- Segmentation by engagement levels: Yeah, I know, I begin sounding like a broken record. But anyway, group subscribers based on their interaction with your emails (e.g., highly engaged, moderately engaged, unengaged). This allows you to tailor content and sending frequency.
- Demographic and psychographic segmentation: Segment based on subscriber demographics (age, location) or psychographics (interests, values) to deliver more targeted content.
- Behavioral segmentation (website activity, purchase history): Create segments based on user behavior on your website, purchase history, or in-app actions. This enables highly relevant, triggered, or personalized communications.
- Dynamic list segmentation techniques: Implement systems that automatically update segments based on real-time user behavior, ensuring your lists are always current.
- Personalization based on segments: Leverage your segmentation data to personalize email templates, content, subject lines, and offers, making each email feel more tailored to the individual. For a full tutorial, check ➡️Email List Segmentation Explained: Tutorial with Examples.
Enhance subscriber preference and unsubscribe handling
Providing clear, easy-to-use options for managing preferences and unsubscribing is crucial for maintaining a healthy list and avoiding spam complaints.
- Implementing user preference centers: Allow subscribers to choose the types of content they receive and the frequency. This empowers them and reduces the likelihood of unsubscribes due to irrelevant content or excessive frequency.
- Prompt and compliant opt-out processing: Process unsubscribe requests immediately without requiring additional steps (like logging in). Failure to do so can lead to spam complaints and legal non-compliance (e.g., CAN-SPAM, GDPR).
- Manage global suppression lists: Maintain a comprehensive global suppression list of all unsubscribed or bounced addresses (ideally, one correctly parsed list across all domains and subdomains you use). This ensures you never accidentally re-add or send to contacts who have opted out or are undeliverable. Here’s a comprehensive guide on How to Manage Your Email Suppression List effectively.
Maintain ongoing data quality and compliance
List management isn’t a one-time task; it’s a continuous commitment to data quality and legal compliance.
- Periodic data accuracy audits and updates: Regularly audit your list for outdated or unnecessary personal data as part of a GDPR data audit, and implement processes that allow subscribers to review and update their information.
- Processes for data subject rights (Access, Rectification, Erasure under GDPR): For global senders, establish clear procedures for handling data subject requests as per regulations like GDPR, including access to their data, rectification of inaccuracies, and the right to be forgotten.
- Staying updated on email marketing regulations: Email regulations (like CAN-SPAM, GDPR, CCPA, and new ISP requirements from Google and Yahoo) are constantly evolving. Stay informed to ensure your practices remain compliant and legal infringements don’t negatively impact your deliverability.
For more guidelines on legal conundrums, go to: Legal Aspects of Email Marketing: Laws, Compliance, and Penalties
Improve email sending practices
Beyond technical setup and list hygiene, how you send your emails—your volume, frequency, and timing—plays a significant role in your deliverability and reputation with ISPs.
Let’s take a look at what you can adjust to achieve a higher inbox placement rate.
Manage sending volume and consistency
ISPs favor senders with predictable and consistent sending patterns. Sudden, unexplained spikes in volume can trigger spam filters.
- Establish consistent, predictable sending patterns: Aim for regular sending schedules. If you typically send weekly newsletters, try to stick to that pattern. Consistent volume helps ISPs learn and trust your sending behavior.
- Avoiding sudden large volume spikes: Unexpected increases in email volume can look suspicious to ISPs, even for established senders. If you anticipate a major campaign, prepare by gradually increasing your volume beforehand, similar to IP warming. Monitor your deliverability metrics closely during ramp-up phases to catch any issues early.
Optimize sending frequency and cadence
Finding the “just right” frequency keeps your audience engaged without leading to list fatigue or spam complaints. How to do it? My best tip is to experiment to determine…
- Optimal email frequency per list segment: It’s not uncommon for different segments of the audience to tolerate different sending frequencies. Analyze engagement data for each segment to fine-tune how often you send to them.
- Tactics to avoid list fatigue: The way to do it is just don’t email unsegmented recipients often. To that, you need to hawk over open rates and unsubscribe rates – a drop often signals fatigue. The same goes for a sudden increase in inactive subscribers.
- The impact of sending cadence on engagement and deliverability: Continuously test and analyze how changes in your sending cadence affect key metrics like open rates, click-through rates, and, crucially, spam complaint rates and deliverability. If you see spikes in negative engagement, your recipients may prefer a slower tempo.
Utilize email throttling and rate limiting effectively
Throttling and rate limiting prevent you from overwhelming an ISP’s receiving servers, which can lead to deferrals or blocks. Anyway, you need to do some homework and some tweaking to get it right. Here’s a set of bullets to get you going.
- Understand ISP receiving limits and feedback: Typically, the receiving limit is around 3,600 emails per hour. Exceeding these limits often results in temporary rejections (soft bounces) or, worse, hard blocks.
- Configure send speed (throttling) in ESP/MTA: Your Email Service Provider (ESP) or Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) should allow you to configure sending rates. Properly setting these limits helps you stay within ISP boundaries.
- Benefits of throttling for high-volume sends: Throttling is a technical practice that controls the rate at which emails are sent over a given period rather than sending a large volume all at once. It ensures your emails are accepted gracefully by ISPs, preventing backlogs and delivery errors, leading to smoother, more consistent deliverability.
Strategic email stream separation
Separating different types of email traffic is a cornerstone for maintaining a good reputation for high-volume senders. But how you separate it depends on your ESP and the email volume. Not all providers offer separate streams. And sometimes, it makes more sense to use a separate dedicated IP on top of separate streams, particularly if you do outreach.
So, check the method to this streaming madness 😀
- Rationale for separating transactional vs. marketing email streams: Transactional emails (e.g., password resets, order confirmations) are expected and critical, while marketing emails are often seen as less urgent. Mixing these can put your critical transactional deliverability at risk if marketing sends face issues.
- Using dedicated IPs/subdomains for different email types: As mentioned in IP and domain reputation, assigning separate dedicated IPs or subdomains for transactional, marketing, and notification emails allows each stream to build and maintain its own reputation independently.
Leverage Send Time Optimization (STO)
Sending emails when your audience is most likely to engage can significantly boost open and click rates, positively impacting deliverability.
- A/B testing send times for different audience segments: Experiment with various send times and days of the week to pinpoint what works best for specific segments.
- Utilizing ESP built-in STO features vs. manual analysis: Many ESPs offer built-in STO features that automatically deliver emails at the optimal time for each recipient. For custom setups, detailed analysis of your own metrics is key.
- Considering time zones for global audiences: If you have a global audience, ensure your send times are optimized for their respective time zones to maximize engagement.
Best practices for email batching and campaign scheduling
You need to properly break down (segment) and schedule large email campaigns. And large, in our experience, typically translates to 10K or more emails a week.
Otherwise, the almost willy-nilly approach can influence how ISPs perceive you as a sender. More importantly, it limits your ability to monitor performance across different funnel stages.
So, here’s what to do.
- Break down large campaigns into smaller batches: Instead of sending a million emails all at once, divide the campaign into smaller, manageable batches. This allows for smoother delivery and easier identification of issues if they arise.
- Intelligent scheduling strategies across peak/off-peak hours: Schedule non-critical bulk sends during off-peak hours for ISPs when their servers might be less congested. Prioritize critical transactional sends during peak times if deliverability is paramount.
- Prioritize critical transactional emails over bulk sends: Ensure your MTA or ESP prioritizes transactional emails in its queue. These are often time-sensitive and have the highest deliverability requirement.
- Monitoring send progress and server responses during large sends: Actively monitor your sending progress and any error responses from receiving servers during large campaigns. This proactive approach allows you to identify and react to potential issues (like throttling or deferrals) in real-time.
Improve email content
Poor content can land your emails in the spam folder, even with the perfect technical setup and a pristine list. So, focus on building trust with the content and avoid triggering spam filters.
Check the hands-on tips and tricks below.
Optimize subject lines and preheaders for engagement and filters
Your subject line and preheader are the gatekeepers to your email’s content. In a lot of cases, they determine if your email is opened or ignored (or worse, marked as spam).
- Avoid common spam trigger words and ALL CAPS: Steer clear of words and phrases commonly associated with spam (e.g., “free money,” “guarantee,” excessive exclamation marks) and avoid using all capital letters, which can appear aggressive and spammy.
To be perfectly honest, Yaroslav, our in-house deliverability expert, identified less of an impact of “spammy” words on campaign performance. However, this finding shouldn’t motivate you to create emails like you’re selling snake oil.
If you need more details and examples of best practices, our guide on 240 Email Spam Words To Avoid When Sending Emails can provide a helpful reference.
Or maybe you want to ⬇️📲…
- Craft clear, concise, and relevant subject lines: Your subject lines should accurately reflect the email’s content, be brief, and clearly communicate value to the recipient.
- Use personalization effectively (names, interests, etc.): If possible, incorporate a recipient’s name or interests into the subject line. This can significantly boost open rates, as it makes the email feel more relevant.
- Maximize preheader text for additional context and intrigue: The preheader text (the snippet of text visible after the subject line in the inbox) should complement your subject line, providing more context or a compelling reason to open.
- A/B test subject lines and preheaders for open rates: Continuously test different subject line and preheader combinations to identify what resonates best with your audience and drives higher open rates.
Write email body copy that builds trust and avoids filters
The body of your email must deliver on the promise of your subject line and maintain recipient trust.
- Balance promotional content with informational/value-driven text: For marketing emails, balance promotional messages with genuinely helpful, informative, or entertaining content. This builds long-term engagement and trust.
- Implement advanced personalization within the body: Go beyond just a name. Use behavioral data, purchase history, or other subscriber attributes to dynamically populate content within the email body, making it highly relevant.
- Ensure proper grammar, spelling, and professional tone: Typos, grammatical errors, unprofessional tone and unoriginal text can undermine your credibility with recipients and spam filters. Always proofread diligently and use a plagiarism checker.
Design HTML emails for optimal deliverability and user experience
A well-coded, responsive HTML email formatting is crucial for a positive user experience, and it helps bypass spam filters.
- Use clean, lightweight HTML code: Complex or broken HTML can trigger spam filters or render poorly. Use clean, minimalist, and standards-compliant code. Avoid excessive inline styling or large amounts of hidden text. Our Free HTML & CSS Email Checker by Mailtrap can help you validate your code.
- Ensure fully mobile-responsive email design: A significant portion of emails are opened on mobile devices. Your emails must render perfectly on all screen sizes to ensure readability and engagement.
- Maintain a healthy text-to-image ratio (avoiding image-only emails): Emails that are primarily images with little text are often flagged by spam filters as they can be used to hide malicious content. Aim for a balanced ratio, with sufficient text. For instance, about 80-20% split in favor of the text.
- Implement ALT text for all images (accessibility and deliverability): Always include descriptive ALT text for your images. This improves accessibility for visually impaired users and provides context if images fail to load.
- Basic email accessibility considerations (WCAG): Beyond ALT text, consider other accessibility best practices (e.g., sufficient color contrast, logical reading order) to ensure your emails are usable by everyone.
Manage links and attachments responsibly
How you handle links and attachments can significantly influence how spam filters perceive your email.
- Link exclusively to reputable and secure (HTTPS) domains: Ensure all links in your email point to legitimate, trustworthy websites secured with HTTPS. Linking to suspicious or unencrypted domains is a major red flag.
- Avoid an excessive number of links or link shorteners known for abuse: Too many links can appear spammy. Also, be wary of generic link shorteners often abused by spammers; branded shorteners are safer. But generally, I’d say avoid shorteners unless absolutely necessary.
- Minimize or avoid attachments in marketing/bulk emails: Attachments are a common vector for malware and are almost always flagged in bulk emails. Avoid them in marketing campaigns entirely. For transactional emails that require attachments, ensure they are absolutely necessary and secure, something like invoices, bills, shipping documents, etc.
- Use clear, descriptive anchor text for hyperlinks: Use descriptive anchor text for your links rather than generic phrases like “click here.” This improves user experience and signals legitimacy.
Set clear Calls-to-Action (CTAs) and compliant unsubscribe options
Your CTAs should be unmistakable, and your unsubscribe options even more so.
- Design clear, prominent, and compelling CTAs: Make it easy for recipients to understand what action you want them to take and where to click. Use compelling language and visually distinct buttons.
- Make the unsubscribe link easy to find, understand, and use (one-click): This cannot be stressed enough. A clear, easily accessible unsubscribe link (usually in the footer) is crucial for avoiding spam complaints.
- Technical implementation of list-unsubscribe header: As previously discussed, implementing the List-Unsubscribe header allows users to unsubscribe with a single click directly from their email client, dramatically reducing complaint rates. For detailed steps on how to avoid emails going to spam, check out our tutorial: How to Avoid Emails Going to Spam: Tutorial.
- Honoring unsubscribe requests as per regulations (GDPR, CAN-SPAM): Immediately process all unsubscribe requests. Delaying this or making it difficult is a clear violation of email marketing laws and will severely damage your sender reputation.
Pro Tip: According to the regulations mentioned above (GDPR, CAN-SPAM), you have up to 10 days to honor the requests. However, users expect it to be immediate, or at least, effective in 24-48 hours. Given the automatic nature of most contemporary email platforms, my suggestion is to delist a recipient as soon as they opt out with a basic trigger-action automation.
Improve email user engagement
Ultimately, deliverability is about consistently landing in the inbox because recipients want your emails. Here’s how to softly nudge users towards engagement.
Maximize positive engagement signals
As mentioned a few times, positive interactions with your emails are highly valued by ISPs. Encouraging these helps build a robust sender reputation. So, consider employing the following.
- Encourage replies and forwards: Emails that generate replies or are forwarded indicate high value. Craft content that sparks conversation or is highly shareable.
- Get emails marked “Important” or moved to the primary inbox: Encourage recipients to manually mark your emails as important or move them from promotions/spam folders to their primary inbox. This is a very strong positive signal to mailbox providers. However, make sure to do it sensibly – for instance, only when a recipient reports your newsletter is getting into the Promotions tab, or elsewhere.
- Promote “Add to Contacts” / whitelisting: Encourage subscribers to add your “From” email address to their address book or whitelist. This virtually guarantees future deliverability. Again, this is something you need to do tactfully, not like a full-on campaign focused on “Add to Contacts.”
Minimize negative engagement signals
Negative interactions can quickly degrade your sender reputation, making it harder to reach the inbox.
- Tactics to reduce spam complaints: The most critical tactic is ensuring clear, informed consent during list acquisition. Beyond that, consistently providing valuable, relevant content and offering an easy, one-click unsubscribe option are paramount.
- Avoiding “delete before reading”: When recipients consistently delete your emails without opening, it signals disinterest to ISPs. Strong sender recognition and consistently valuable, intriguing subject lines are crucial to avoid this.
Drive engagement with advanced personalization and segmentation
Tailor your communication to make emails more relevant, leading to higher engagement and better deliverability. Here are the pointers.
- Use behavioral triggers for highly relevant, timely emails: Implement email automation based on user actions (e.g., abandoned cart reminders, post-purchase follow-ups). These triggered emails are highly relevant and often have exceptional engagement rates.
- Implement dynamic content based on user data and preferences: If possible, leverage your ESP’s capabilities to insert dynamic blocks of content into emails based on individual subscriber data, preferences, or behavior.
- Personalization techniques beyond basic merge tags: Go beyond just using a recipient’s first name. Incorporate purchase history, browsing behavior, lifecycle stage, or product recommendations for deeper personalization.
Enhance content value and relevance to boost interaction
The intrinsic value of your email content is the ultimate driver of engagement.
- Provide exclusive content or early access: Offer your email subscribers unique benefits or information unavailable elsewhere. This incentivizes opens and clicks.
- Use storytelling and creating emotional connections: Engaging narratives and content that resonates emotionally can significantly increase the reading time and the likelihood of interaction.
- Ensure a clear value proposition in every email: Before sending, ask yourself: “What value does this email provide to the recipient?” Make that value proposition clear and compelling.
- Align email content with the subscriber’s journey stage: Ensure the content matches where the subscriber is in their customer journey (e.g., onboarding, consideration, loyalty).
Optimize send timing and frequency for peak engagement
Even the most perfect email can be missed if sent at the wrong time.
- A/B test different send times and days of the week: Continuously experiment with various send times and days to identify when your audience segments are most active and receptive.
- Utilize Send Time Optimization (STO) tools or features: Many ESPs offer STO capabilities that use algorithms to predict the best send time for each individual recipient based on their past engagement patterns.
- Respect user-stated frequency preferences (via a preference center): If you offer a preference center (as discussed in Enhancing subscriber preference and unsubscribe handling), rigorously adhere to the frequency choices made by your subscribers.
- Adjust sending cadence based on individual engagement levels: For unengaged segments, reduce sending frequency or pause sends altogether to avoid negative signals and potential spam complaints.
Incorporat interactive elements and direct feedback (Advanced tactic)
For tech-savvy senders, interactive elements can supercharge engagement. Mind you that some of these actions may require you to have decent programming skills. Or simply, you can ask a developer for help.
- Explore AMP for email for in-mail actions (polls, forms): AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) for email allows recipients to complete actions like filling out forms, answering polls, or browse products directly within the email client, without leaving their inbox.
- Embed simple surveys or polls for feedback: Directly ask for feedback within the email to gauge satisfaction or gather insights(e.i. You could use open-ended questions with a small incentive for the participants). This demonstrates you value their opinion and encourages interaction.
Email deliverability monitoring: your continuous feedback loop
Without consistent tracking of key metrics, you’re sending emails into a void, unaware of how they’re truly performing. For high-volume senders, this means having robust systems in place to provide real-time insights and diagnostics.
Key deliverability metrics to track
To maintain a healthy email program and ensure your emails reach the inbox, focus on these critical metrics:
- Inbox placement rate: This is the ultimate metric. It tells you the percentage of your emails that successfully land in the primary inbox, as opposed to the spam folder, promotions tab, or being rejected entirely.
- Open rate: While not a direct deliverability metric, a consistently low open rate can signal engagement issues that may eventually affect your sender reputation. It indicates whether your subject lines and sender name are resonating.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Similar to open rates, a healthy CTR indicates that your content is relevant and valuable, which positively influences engagement signals.
- Bounce rate: Track hard bounces (permanent delivery failures) and soft bounces (temporary issues). High bounce rates, especially hard bounces, severely damage your sender reputation. Automated removal of hard bounces is non-negotiable.
- Spam complaint rate: This is one of the most damaging metrics. A high rate indicates that recipients are actively marking your emails as spam, which significantly degrades your sender reputation with ISPs. Aim for rates well below 0.1%.
- Unsubscribe rate: While not as damaging as spam complaints, high unsubscribe rates suggest list fatigue or irrelevant content. Monitor this to understand subscriber satisfaction.
- Blocklist status (IP and domain): Regularly check if your sending IPs or domains are listed on any major public or private blocklists. Being listed is a strong indicator of deliverability issues. As mentioned, Mailtrap offers Free IP Blacklist Checker and Free Domain Blacklist Checker.
- Authentication failure rates (SPF, DKIM, DMARC): Monitor DMARC reports for authentication failures. A high number of failures suggests misconfigurations or, more seriously, unauthorized use of your domain (spoofing).
- ISP-specific feedback (Google Postmaster Tools, Microsoft SNDS): These invaluable tools provide direct insights from major mailbox providers on your domain and IP reputation, spam rates, and authentication errors specific to their ecosystems. Regularly check these dashboards for any warnings or changes in your sender health.
Utilizing monitoring tools for insight
For high-volume senders, manual checks aren’t enough. You need comprehensive tools that offer detailed analytics and actionable insights.
- Mailtrap’s deliverability analytics: As an email sending platform, Mailtrap provides in-depth analytics that are crucial for monitoring your deliverability. Our dashboard allows you to:
- Track key sending metrics over time, including delivery rates, open rates, click rates, and bounce rates.
- Monitor ISP engagement and performance across different mailbox providers.
- Identify potential issues with detailed logs and reports that show why emails might be bouncing or failing authentication.
- Gain visibility into DMARC reports, helping you identify authentication alignment issues or detect unauthorized sending from your domain.
- Email spam checkers: Before sending critical campaigns, use a tool like Mailtrap’s Email Spam Checker to assess your email’s likelihood of being flagged as spam by various filters. This proactive check can save you from widespread delivery failures.
Further reading: How to Test Email Deliverability & What Tools to Use [2025]
Proactive actions based on monitoring data
Monitoring is only half the battle; the other half is acting on the data.
- Analyze bounce logs and FBL data: Regularly review detailed bounce logs to understand the specific reasons for delivery failures. Combine this with FBL (Feedback Loop) data to identify and promptly remove complainers from your list.
Note: Some ISPs won’t readily share FBL data for security reasons, so your best bet is using tools like Postmaster, SNDS, and similar.
- Interpret DMARC reports for alignment issues: DMARC reports provide vital information on emails failing SPF or DKIM authentication and whether they’re aligned with your domain. Analyze these reports to fix misconfigurations or detect spoofing attempts.
- Regular sender reputation audits: Conduct periodic audits of your sender reputation, utilizing all available tools and data.
Mastering the inbox: trust deliverability
Congrats! Together, we’ve walked through the intricate world of email deliverability, from the foundational technical configurations to the nuanced art of user engagement.
For high-volume email senders and the software engineers supporting them, mastering these elements is not merely about avoiding the spam folder; it’s about ensuring your critical communications reach their intended recipients, fostering trust, and driving tangible business outcomes.
And remember, email deliverability is a marathon, not a sprint; a continuous cycle of implementation, monitoring, analysis, and adaptation.
With diligence, commitment to best practices, and the right tools at your disposal, you can build and maintain the sender reputation needed to earn the inbox’s trust, ensuring your messages always hit their mark.