Optimizing email marketing goes beyond generic tips and best practices. To do it right, you need to focus on refining, iterating, and changing your approaches to strategy and individual email sequences.
The idea is to leverage data-driven processes to fine-tune segmentation and content structure and keep testing marketing strategies. And it doesn’t matter if you’re an enterprise marketer or a solopreneur; the sooner you start, the better.
Here, I’ve listed seven strategies for effective email marketing optimization. I’ll walk you through the key areas of optimization, which include analyzing vital metrics, designing email templates, and automating email campaigns.
Email marketing optimization: a snapshot
Email marketing optimization is the continuous process of refining the elements of your email marketing campaign to maximize ROI and overall campaign performance.
The iterative workflow combines behavioral insights, customer data analysis, and A/B testing to optimize send times and enhance automation. Each adjustment in email subject lines, calls to action, content formats, and personalization approaches aims for higher email engagement.
At its core, optimization mainly focuses on:
- Subscriber retention
- Conversions
- Intent signals
- Post-click behavior
- Responsiveness
According to The State of Email 2025 report by Litmus, one-third of companies achieve an email marketing ROI between 10:1 and 36:1, and another third achieve an ROI above 36:1.
Such ROI depends on how well-optimized every facet of your email strategy is. Let’s get a closer look at the key areas that contribute to it.
Email list management optimization
Email list management optimization refers to refining your subscriber list based on the analysis of their behavior and responsiveness.
Metrics for optimization
- Bounce rate: Emails that did not reach the inbox due to server issues and invalid email addresses. Keep it below 2%.
- Growth rate: Percentage of new email subscribers added after filtering the list. Calculation goes like this: (New subscribers – Unsubscribes / Total subscribers) x 100
- Spam rate: Percentage of recipients marking your email as spam. Must stay < 0.1%.
How to track metrics
- ESP reports: Leverage email service providers like Mailtrap to use built-in tools for tracking email open rates, bounce rates, and deliverability in real-time.
- UTM: Implement UTM codes in URLs to connect email clicks to on-site actions via Google Analytics.
- Dashboards: Export metrics (e.g., open, click, and bounce rates) to BI tools like Looker Studio, Tableau, or Microsoft Power BI. These external dashboards help you spot trends by cross-referencing email performance with CRM or sales data. This makes it easier to understand engagement patterns and manage your list more effectively.
How to optimize
- Double opt-in: Apply a double opt-in framework to validate subscribers joining your list.
- Prune disengaged subscribers: Preset disengagement thresholds, such as not opening emails for 90 days. Then, remove inactive users to enhance list quality. You can also try a reengagement campaign before the 90-day period expires, which may allow you to prune unresponsive recipients even sooner.
- Segmentation tags: Segment recipients based on predetermined factors like engagement history, demographics, and purchase patterns.
How to interpret the results of optimization tests
- Statistical significance: Use statistical methods and calculations to ensure reliable test results and not random choices. Here are the standard formulas to interpret campaign performance.
| Metric | Formula | Interpretation |
| Open Rate | Unique OpensEmails Deliveredx 100 | Signals how effective your subject lines are. |
| Click-Through Rate | Unique Clicks Emails Deliveredx 100 | Signals the relevance of the email content and messaging. |
| Conversion Rate | ConversionsEmails Deliveredx 100 | Signals a campaign’s effectiveness. Make sure to define conversion based on the email type. |
| Bounce Rate | Bounced EmailsEmails Sentx 100 | Signals deliverability, but also email list health |
| Unsubscribe Rate | UnsubscribesEmails Deliveredx 100 | Signals the health of your email list and can relate to content relevance. |
| ROI | Campaign Revenue – Campaign CostCampaign Cost x 100 | Shows campaign profitability. |
- Iteration: Consider insights of both pre-and post-optimization metrics to make informed adjustments in the next round of optimization. For example, if pruning inactive subscribers improves open rates but increases unsubscribe rates, adjust your list cleaning frequency and re-engagement email timing. A/B testing and segment analysis help you do that efficiently.
Email deliverability optimization
Email deliverability optimization is a dedicated process to improve the probability of your emails landing in the recipient’s inbox.
Metrics for optimization
- Spam rate: Percentage of emails marked as spam by in-built mechanisms of the mailbox or by the recipient.
- Sender reputation: Domain’s credibility as evaluated by mailbox providers.
- Deliverability rate: Percentage of emails reaching inboxes, showcasing sender reputation.
- Bounce rate: Percentage of emails not delivered due to invalid email addresses or server issues.
How to track metrics
- Deliverability tools: Use analytical platforms to perform advanced tracking, ensure inbox placement, and maintain sender reputation.
- Authentication reports: Monitor DNS settings, which include SPF, DMARC, and DKIM through domain management tools to reduce spam filtering.
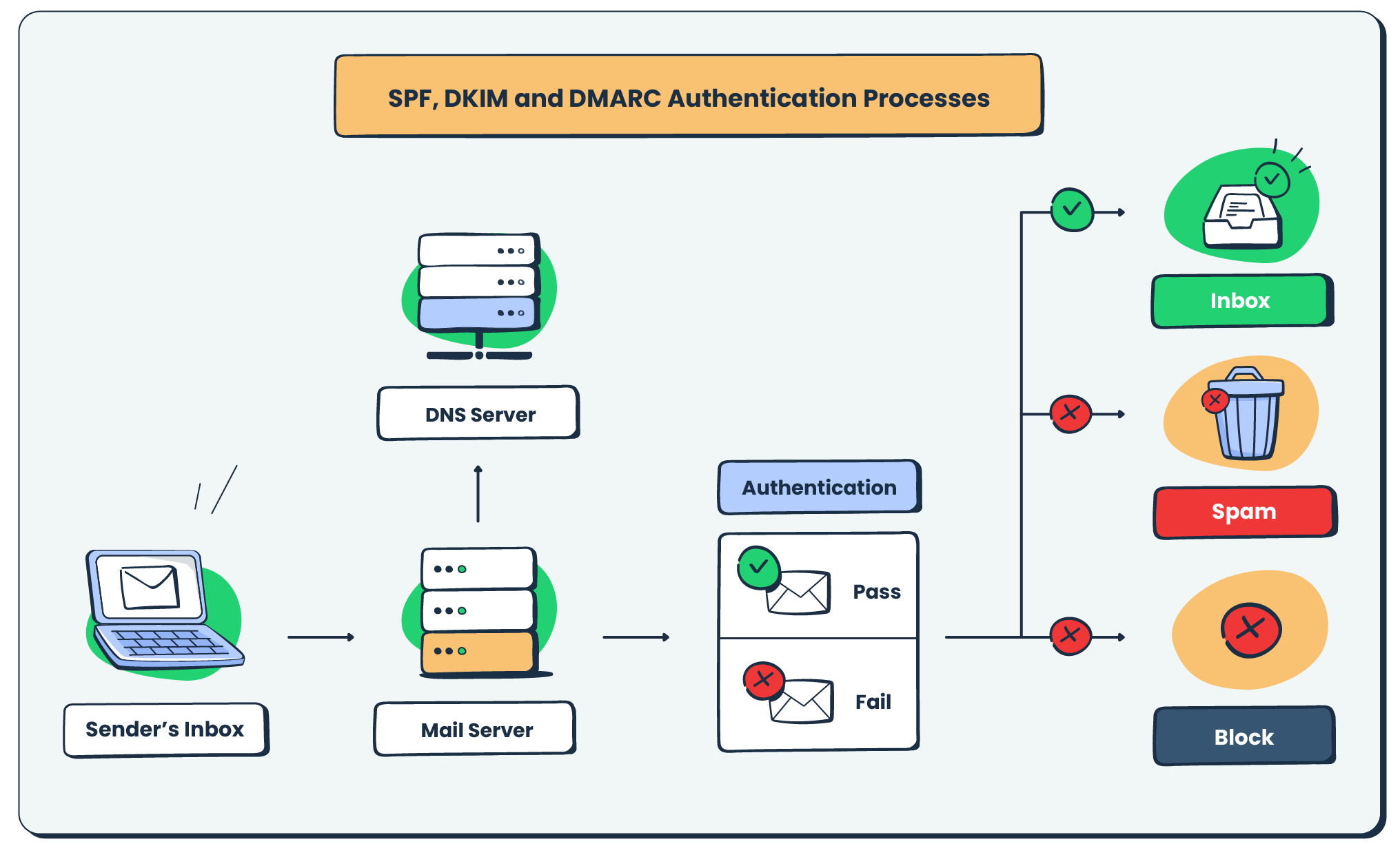
- Framework: Set up bounce handling and feedback loops to track rejections and spam flags programmatically.
How to optimize
- Content quality: Don’t include spammy language, misleading subject lines, irrelevant visuals, and misaligned formatting.
- Originality: Ensure your email content is original and trustworthy, you can use the best plagiarism checker to prevent spam filters from flagging duplicated content.
- Testing: Run A/B tests on subject lines, content, and send times to identify what improves deliverability.
- Audit: Regularly remove invalid, inactive, or bounced addresses to reduce bounce and increase deliverability.
How to interpret the results of optimization tests
- Identify patterns: Spot similar trends by comparing the before and after outcomes of optimization. For example, improved open rates after subject line optimization.
- Monitoring: As discussed earlier, optimization is a continuous process, which means you must continuously track metrics over time for early identification of issues to keep pace with evolving mailbox algorithms.
- Negative signals: Track upward shifts in negative signals, such as bounce rate, spam complaints, or unsubscribes, to identify negative consequences of optimization, if any.
Email sending optimization
Email sending optimization refers to refining how and when you send emails to maximize engagement and improve KPIs.
Metrics for optimization
- Engagement patterns: Monitor how recipients engage with emails based on distinct sending frequencies. This includes actions like opening emails, clicking on links, and converting to a paid customer.
- Click-to-open rate (CTOR): Percentage of people who click on the link in the email. This metric is generally larger than the click-through rate (CTR).
- Performance: Measures open, click, and conversion rates based on the time and day emails are sent. It also includes the percentage of recipients who complete a desired action after receiving the email.
How to track metrics
- Heatmaps: Use heatmaps to visualize important data such as location and time of emails being opened and clicked.
- Marketing dashboards: Utilize a reliable ESP, like Mailtrap, that offers built-in analytics dashboards to closely monitor send times, frequency, and other engagement metrics discussed earlier.
- API integration: Integrate the ESP dashboard with CRM, ecommerce stores, and automation tools to facilitate real-time tracking of list growth and conversions.
How to optimize
- Manual segmentation: Export analytics data into a spreadsheet or a BI tool to analyze engagement and send trigger actions based on recipient behavior.
- A/B testing: Consider A/B testing to experiment with sending frequency. Compare engagement across different sent times and cadences to determine an optimal pace. At the same time, pay attention to unsubscribe and spam rates.
- Isolate variables: Continuously run controlled experiments, adjusting only one variable at a time (send time, frequency, segment) to isolate impact.
How to interpret the results of optimization tests
- Contextual insights: If a new send time improves open rates but not conversion rates, examine the alignment of your email content with user pain points.
- Performance analysis: Analyze which send times or frequencies yield the highest open, click, and conversion rates. Look for consistent patterns across multiple tests.
- Statistical approach: Once the tests reach a sufficient sample size (e.g., ~1000 recipients per test, or more, depending on your scope and reach), apply statistical methods to validate the reliability of the observed results. Here are the methods you could use.
| Method | Description | When to use the method |
| Hypothesis testing (Z-test, t-test) | Compares proportions (e.g., open rates, click rates) between two groups to see if the differences are statistically significant. | Most common for comparing metrics like open rate or click-through rate between two email variants. |
| Chi-Square test | Tests independence between categorical variables (e.g., conversion vs. no conversion across groups). | Useful for categorical outcomes such as conversion rates or unsubscribe rates. |
| Confidence Intervals (CI) | Provides a range within which the true metric difference likely falls, with a given confidence level (usually 95%) | Helps quantify uncertainty around observed differences and assesses practical significance. |
| Bayesian analysis | Uses prior knowledge and observed data to estimate the probability that one variant is better than another. | Increasingly popular for continuous learning and decision-making under uncertainty in marketing tests. |
| Statistical power analysis | Determines if the sample size is sufficient to detect a meaningful difference with high probability. | Ensures tests are designed to avoid false negatives (Type II errors) and are adequately powered. |
Email content optimization
Email content optimization is the process of improving the structure, layout, and language of email messages based on measurable outcomes.
Metrics for optimization
- Scroll depth: Measures how far recipients scroll through your email content, indicating content engagement.
- Time spent reading: This showcases content relevance and readability by measuring the average time spent reading the email content.
- Reply rate: Refers to the number of direct replies from recipients, which is important for conversational and feedback analysis.
How to track metrics
- Web analytics: As mentioned earlier in the article, implement UTM codes in email links to track conversions and time spent on the page using Google Analytics.
- Custom tracking: Embed tracking pixels, a tiny, invisible image embedded in the HTML of an email, are useful for measuring time spent and scroll depth. However, some providers, like Apple Mail and ProtonMail, block or pre-load these pixels, inflating the open rate and distorting time-spent data. To account for this, review provider policies to adjust your approach and prioritize more reliable action-based metrics like click-through rates.
- Manual tagging: For reply and share rates, use unique reply-to addresses or share buttons with trackable URLs. For example, instead of a generic email address, like reply@yourcompany.com, use reply-campaign1@yourcompany.com.
How to optimize
- Personalization: Gather the recipient’s data and include their names, preferences, and personalized content blocks, like product recommendations, banners, or images tailored to their interests or past behavior (reverse image search tools can be helpful in this case). These blocks add visual variety and break up walls of text, making the email more engaging.
- Content hierarchy: Follow a standard content structure. A typical content hierarchy looks like this:
- Header: Benefit-driven headline
- Subheader: Extend the headline and lay the foundation of the main message
- Email copy: Scannable content with straightforward points
- Visuals: Images relevant to the main message
- CTA: A big, action-focused button
- Readability: Test different font sizes, contrast ratios, and alt text to ensure content is accessible and engaging for all users.
How to interpret the results of optimization tests
- Isolate impact: Compare the performance of variants by considering CTOR, conversion rates, and time on page. Identify which variant drives the most conversions.
- Segmented insights: Analyze results by audience segment (e.g., device, location, behavior) to uncover content preferences within subgroups.
- Holistic engagement: Ensure alignment throughout the email. For example, a good CTOR with reduced conversions indicates a disconnect between email content and the landing page.
Email design optimization
Email design optimization refers to enhancing your emails’ visual and structural elements to drive more engagement.
Metrics for optimization
- Time spent: This indicates the average time spent viewing your email, which showcases the effectiveness of the email design. (Tip: Email mapping software typically also provides time spent viewing data)
- Unsubscribe rate: Percentage of subscribers who unsubscribe after viewing your email. This signals user experience (UX) issues and poor content structure.
- Load times: Monitors image load times within the email, indicating successful rendering of visuals.
How to track metrics
- Testing tools: Use advanced tools to test diverse design elements and examine how the combination of changes impacts user engagement. Mailtrap Email Sandbox is one such tool, providing hints on how to improve individual email elements.
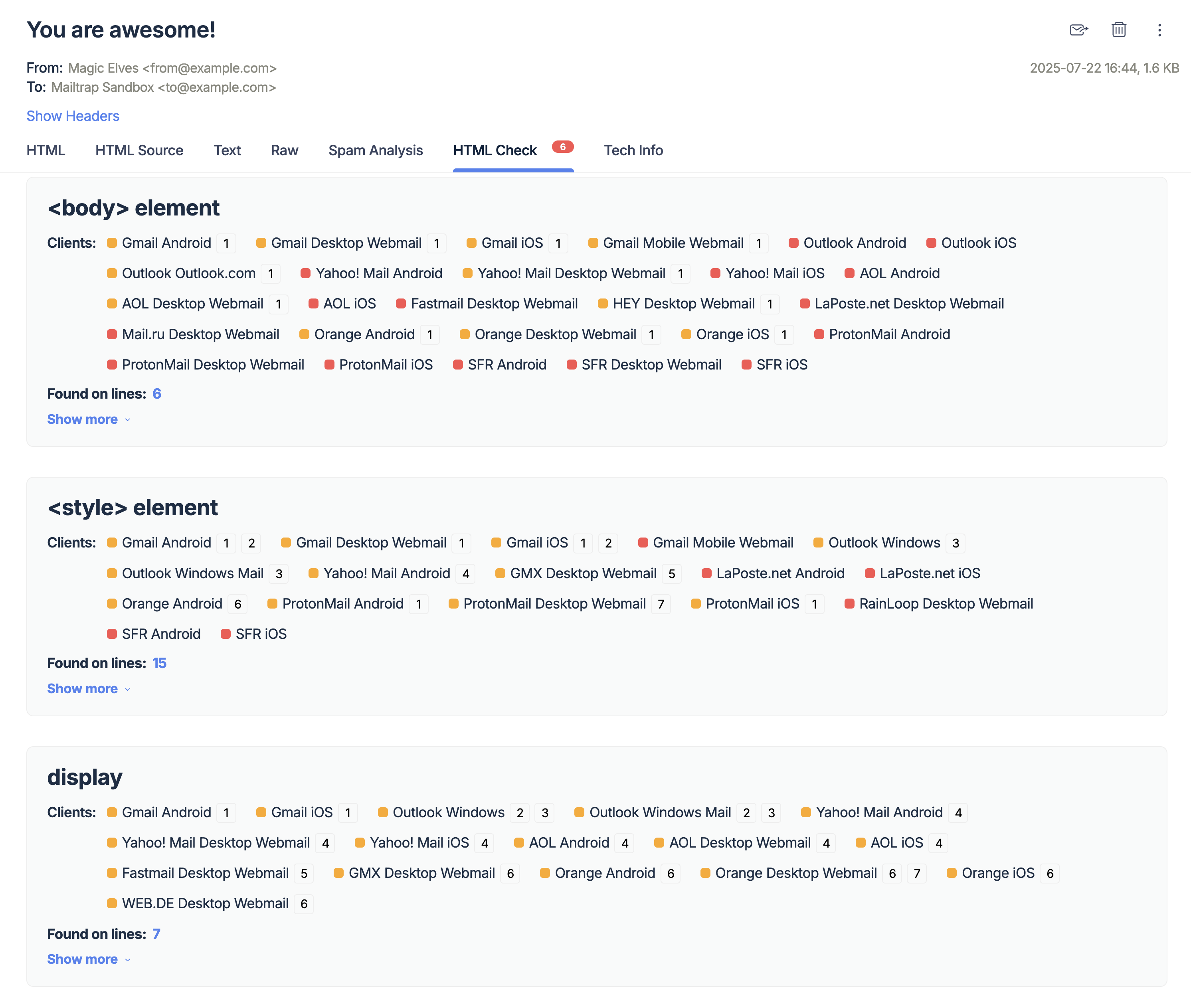
- Tracking tools: Employ analytical platforms to identify elements that receive the most traction from users.
- ESP dashboards: Leverage built-in analytics to automate tracking of essential metrics like unsubscribe rates, CTOR, and CTR.
How to optimize
- Visual hierarchy: Refine the order of visual elements. The key aspects of visual hierarchy are:
- Header: Captivating headlines
- Content layering: Place the main message above the fold
- Typography: Distinct font sizes for each element
- Color and contrast: Highlight CTAs and key pointers
- Whitespace: Improves readability
- Mobile optimization: Adjust layouts, font sizes, and visuals to ensure optimal responsiveness and successful rendering on smaller screens.
- Branded visuals: Align design elements with your brand guidelines and test the impact of consistent vs. experimental visual styles.
How to interpret the results of optimization tests
- Behavioral insights: Analyze heatmaps and scroll data to identify design bottlenecks or areas of high engagement, informing further iterations.
- Iterative refinement: Treat each optimization as a new baseline, continuing to test and refine based on evolving engagement patterns and user feedback.
- Benchmark comparison: Regularly compare your design-driven metrics against industry standards to contextualize performance and set realistic goals.
Email conversion rate optimization
Email conversion rate optimization focuses on increasing the percentage of recipients who complete a desired action after opening your email.
Metrics for optimization
- Conversion rate: Percentage of recipients who complete a predefined goal (e.g., purchase and sign up) after clicking through from your email.
- Revenue per email (RPE): Average revenue generated per email sent, useful for e-commerce and direct sales campaigns.
- Post-click conversion rate: Percentage of users who convert after landing on your website from the email.
How to track metrics
- ESP tracking: Utilize email platforms like Mailtrap to leverage their built-in mechanisms for tracking conversions.
- Event tracking: Preset custom events, such as form submissions and purchases, in the analytics platform to record micro and macro conversions.
- Funnel visualization: Build funnels that show each step from email open to final conversion, highlighting where users drop off.
How to optimize
- Landing page alignment: Ensure alignment between the email’s message, landing page, or social media profile. Test landing page variants to assess email traffic.
- Offer optimization: Experiment with different incentives, like discounts, free trials, and limited-time offers, to measure shifts in conversion rates.
- Follow-up sequences: Optimize and test automated follow-up emails to recover conversions for abandoned carts or incomplete signups.
How to interpret the results of optimization tests
- Funnel analysis: Don’t just prioritize the final conversion rate. This means assessing micro-conversions and drop-off points to make necessary improvements.
- Segmented insights: Break down outcomes based on predetermined segments, like demographics, purchasing history, and user lifecycle, to uncover hidden issues.
- Isolate impact: To know what caused the change in conversions, test one element at a time, like CTA buttons or headlines. Use a control group to compare results and measure the real impact accurately.
Email automation optimization
Email automation optimization is about automating logic, timing, personalization, and email triggers to achieve maximum impact without manual intervention.
Metrics for optimization
- Flow engagement rate: Combined performance of all emails within an automated workflow. It is calculated as: Flow engagement rate = (Total engagements/ Total emails delivered) x 100.
- Completion rate: Percentage of recipients who complete the entire sales funnel through automation without unsubscribing.
- Drop-off rate: Percentage of recipients who exit or stop engaging at each step of the automation.
How to track metrics
- Cohort analysis: Monitor performance for discrete audience segments or entry points to identify trends and optimization opportunities.
- Revenue attribution: Integrate your ESP with your e-commerce or CRM platform to directly attribute revenue to specific automation flows.
- Automation analytics: Build and test your automated flows using Mailtrap’s sandbox environment, which lets you safely validate the email template, CTAs, personalization, and relevant content before going live.
How to optimize
- Refine triggers: Ensure workflows are activated by meaningful, behavior-based events (e.g., cart abandonment vs. just visiting).
- Timing adjustment: Experiment with delays between emails to find the optimal time that maximizes engagement and minimizes drop-off.
- Content personalization: Leverage user data to deliver automated emails tailored to different audience segments.
How to interpret the results of optimization tests
- Step-by-step attribution: Spot the changes that yield measurable improvements in engagement, RPE, and conversions.
- Drop-off analysis: Examine cohort and funnel data to pinpoint points where recipients usually disengage. Focus on optimizing these drop-off points.
- Cumulative assessment: Evaluate the total value generated by the entire automation sequence and the incremental lift provided by each optimization.
Turning metrics into action
Email marketing optimization isn’t a one-time fix but a continuous process focusing on the right metrics. You have to build a robust system that learns, adapts, and performs in real-time to improve key metrics.
I believe optimization really happens when you consider it an iterative framework for testing email variants and aligning with your business goals. Focus on the key areas of optimization outlined in this blog to empower your email marketing efforts.
Visit Mailtrap.io today and optimize emails with advanced analytics and actionable dashboards.