Effective May 5, 2025, Outlook’s new requirements update impacts high-volume senders, or those who send more than 5,000 emails per day.
In this article, I’ll tell you why Outlook is implementing the new requirements and then break them down one by one, explaining how to comply with each.
To jump ahead to the detailed overview of the update, click here.
Why is Outlook implementing new email-sending requirements?
To quote Microsoft, the new email-sending requirements are there to “significantly reduce the likelihood of spam and spoofing campaigns reaching their user base.”
It’s also worth mentioning that these practices are far from new since they’ve existed for quite a while now. Other email giants like Gmail and Yahoo also implemented their own email-sending rules last year.
Moreover, many high-volume, or bulk, senders are already following them, with the biggest difference being that they’ll be required from now on.
It’s also worth mentioning that currently, the update only concerns consumer mailboxes (e.g., outlook.com, live.com, hotmail.com). However, in the future, it will probably be expanded to corporate mailboxes (e.g., 365.com) as well as senders with a volume of less than 5,000 emails/day.
So, if you plan on sending emails with Outlook and don’t want them to be rerouted to Junk folders, it’s recommended you adhere to these practices.
Also, the cost of undelivered emails is not neglectable since you lose $0.11 for every email that doesn’t reach the main inbox.
Detailed overview of the Microsoft sender updates
Outlook’s new update can be divided into email authentication requirements and deliverability recommendations.
Email authentication requirements
The email authentication requirements introduced are primarily concerned with the authentication protocols for address authorization, message authenticity verification, and additional layers of security.
If you don’t meet these requirements after May 5, 2025, Outlook will route your messages to Junk.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
SPF is a protocol dedicated to IP address authorization checks. It validates emails by verifying they are sent from authorized domains/IPs and helps protect against spoofing.
Outlook requires that:
- Your domain’s SPF must pass for the sending domain.
- The IP address or service you use to send emails must be listed in your domain’s SPF DNS record.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
DKIM is a protocol for message authenticity verification. It adds a digital signature to each email, which is one of the most common methods of authenticating yourself as the sender.
Outlook requires that emails you send must have a valid digital signature that matches your domain. Basically, your signing domain should match or align with your From domain.
For example:
- From: john.doe@example.com
- DKIM-Signature: d=example.com
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance)
DMAR is a policy-based email security protocol that utilizes both SPF and DKIM to validate each received message even further. What’s more, it was designed back in 2012 by engineers from leading email organizations (e.g., Microsoft, Google, Yahoo, etc.).
Outlook requires that the emails you send must pass either SPF, DKIM, or both and be aligned with your domain.
- Additionally, you also need a DMARC policy (at least p=none) published in your DNS.
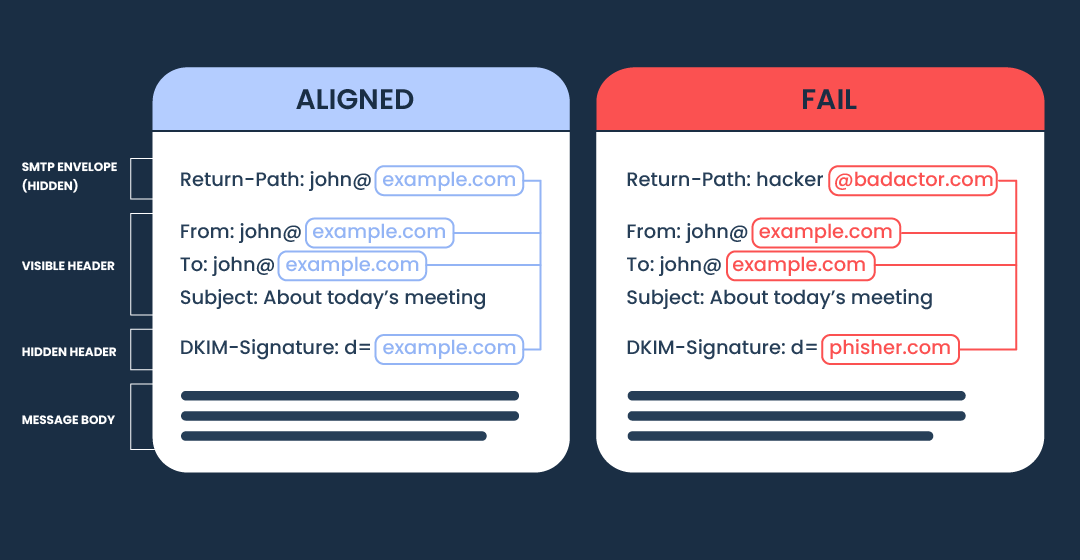
Your From: header domain should match the domain authenticated by SPF or DKIM.
This means that your Return-Path, From, and DKIM domain (d=) must all match the SPF/DKIM authenticated domain.
So, for example, if your authenticated domain is @example.com, then:
- Return-Path: john.doe@example.com → SPF domain = example.com
- From: john.doe@example.com → visible sender = example.com
- Hidden header, DKIM-Signature: d=example.com → DKIM domain = example.com
Email deliverability recommendations
To ensure your email deliverability is high, that is, that your emails land in recipient’s main inboxes, Outlook included some best practices in the update as well.
Although you won’t get routed to Junk if you don’t adhere to them, your email deliverability might suffer if you don’t, meaning your emails might get blocked or filtered.
Compliant P2 (Primary) Sender Addresses
Simply put, your recipients need to be able to reply to the emails you send them from your “From” and “Reply-To” addresses.
This means that addresses like “no-reply@example.com” are not allowed anymore.
Visible and functional unsubscribe links
Although there is no need for RFC 8085 or a one-click unsubscribe button, as with Gmail and Yahoo, Outlook does require your unsubscribe link to be visible. It must not be hidden or tucked away at the bottom of your emails in super small font.
List hygiene and bounce management
Outlook recommends cleaning your list and validating your emails regularly. If not, then at least monthly or quarterly, which aligns with the industry-best practices.
This includes removing faulty and inactive addresses to reduce spam complaints, bounces, and wasted emails.
Some of the tools I recommend (and personally use) for this are:
For a detailed guide on email list hygiene, feel free to check out our dedicated article. ⬅️
Transparent email-sending practices
Your recipients need to have consented for your messages, which also need to include honest subject lines, headers, and valuable content.
We also have a fresh guide on subject lines, so be sure to give it a read.
Mailtrap to the rescue!
Mailtrap is an Email Delivery Platform designed for product companies with high sending volumes.
When it comes to the new Outlook update, we can help you in the following ways:
- Email authentication – We require each sender to have proper authentication (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) before they start to send so each domain is properly checked and prepared.
- Spam complaints – Our Deliverability Team systematically monitors the number of spam complaints and proactively assists customers with their issues to ensure compliance.
- There’s also the free deliverability consultation with one of our experts.
- Detailed Outlook stats – We provide you with performance breakdowns for each provider, including Outlook. These are open rates, spam rates, bounces, and more.
- Dedicated Bulk Stream – Our Bulk Email Service is designed for high-volume senders and can handle large amounts of emails without a stutter, all the while keeping your deliverability high.
- To each email you send through the Bulk stream, we automatically add a one-click unsubscribe button.
And if you’re interested in reading more about Outlook, we have a plethora of related articles on our blog, some of which include:
- Outlook SMTP Explained
- Outlook Spam Filter
- Create an Email Template in Outlook
- Office 365 SMTP
- Send Mass Email in Outlook