Yeah, email still remains one of the most powerful marketing channels, with nearly 4.5 billion users worldwide.
I know, you’re thinking: “I’ve read this a gazillion times, so what?”
Okay, before you write us off as just another post, let me broaden the horizon a bit.
It’s not about the reach. The impressive return on investment (ROI) of $36 per dollar spent, only comes if you understand how to automate and personalize the email workflows.
And to do that, it’s essential to understand and map out the customer journey.
So, in this guide, I’ll explore:
- What an email marketing customer journey entails.
- How to create an effective email marketing customer journey map.
- Practical strategies for designing email campaigns that resonate with your audience at every stage of their journey.
Buckle up!
What is an email marketing customer journey?
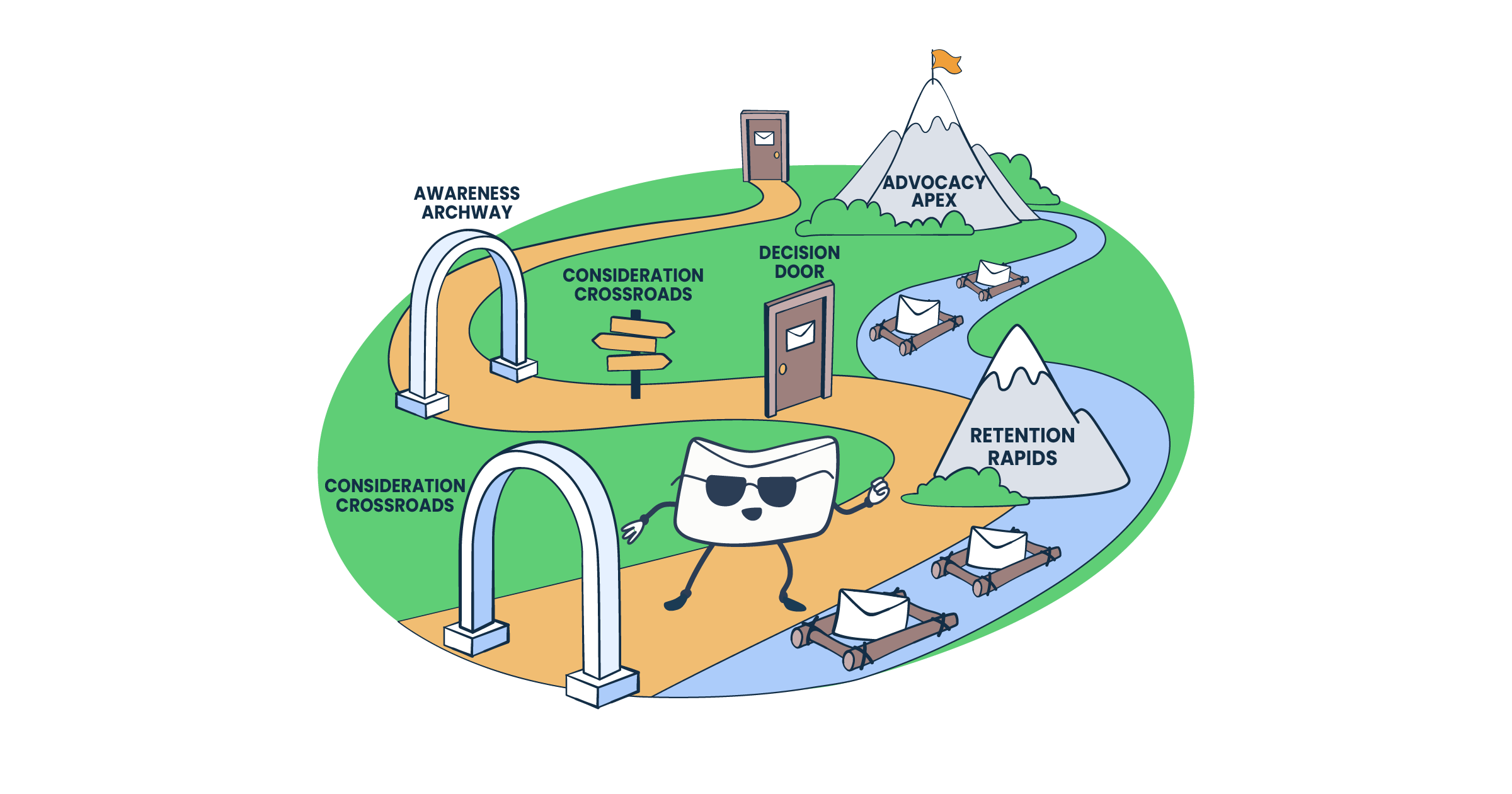
An email marketing customer journey represents all the steps (called touchpoints) a user takes with your brand, from brand awareness to becoming your evangelist.
These journeys (steps) are often delivered as a series of emails, each crafted to nurture familiarity and trust.
To put it plainly, email marketing is an integral part of the customer journey as a whole, with a strong focus on the email touchpoints and their relationship with the recipients (typically users or leads).
Where does email marketing stand in the customer value journey?
Email marketing fits into every stage of a customer value journey, and here’s how you can use its power at every stage:
- Awareness: Embed email capture forms on blogs, social media, and landing pages to raise awareness of your newsletter and value proposition. But remember, you can’t email anyone unless they explicitly opt in.
- Consideration: Send a welcome series after signup. Introduce your brand, share resources, or testimonials. If someone adds items to the cart but doesn’t buy, trigger an abandoned cart email to remind them. The same goes for free trials; it would only be like an abandoned trial drip sequence. At this stage, you could offer more free resources highlighting the product benefits, ask for a survey, or just have a charming sunset sequence.
- Decision/purchase: Send transactional emails like order confirmations, shipping updates, password and security info, and thank-you notes. These reassure customers with details and even promote their next purchase.
- Retention: After a sale, focus on keeping loyal customers. Email a product recommendation or usage tutorials with personalized emails. High-authority, industry newsletters also work well at this stage.
- Advocacy: Turn happy customers into advocates, request reviews or referrals. For example, send a review request email (with a form or button) and seriously consider offering a small incentive.
Note: Each email should feel helpful, not pushy. You must match the message, tone, and call-to-action to the stage (discussed in detail later). The goal is to move people smoothly from one phase to the next without random blasts or confusion.
Why use a customer journey map for email marketing?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of every interaction a customer has with your brand, from first contact to becoming a loyal advocate. It’s a record of your customers’ experiences, emotions, and needs at each stage.
Consequently, a mapped-out journey can significantly support all your marketing channels, and email is just one of them.
But don’t take my word for it, let’s shop around for opinions.
Dave Hockly, founder of Data Story, says “the customer journey isn’t linear” is a common excuse marketers give to run messy, unstructured campaigns. He argues that treating the customer journey as an ‘orbit’ is an unnecessary overcomplication:
And I agree, particularly regarding the B2B space.
The sales cycles are long and crooked, but you still need a clear structure, with different campaigns and messaging tied to real customer stages. In the B2B and FinTech space, understanding the customer journey requires staying ahead of evolving payment trends, as these shifts directly impact how users convert at the decision stage.
Assuming the above was enough of a persuasion, I’ll show you how to utilize customer journey mapping for email marketing:
- Map each stage to specific email goals: Start by aligning each journey stage (i.e., awareness, consideration, purchase, retention, and advocacy) with a clear email objective.
Something like this:
| Stage | Email Objective |
| Awareness | Capture attention and encourage signup |
| Consideration | Educate, nurture, and build trust |
| Decision/purchase | Drive conversions and provide assurance |
| Retention | Deliver value, encourage repeat usage |
| Advocacy | Encourage reviews, referrals, and social sharing |
Pro Tip: Your map should include real customer pain points, triggers, and decision criteria, and these should directly shape email copy and offers.
- Create trigger-based campaigns from key touchpoints: Use a journey map to identify high-impact moments (actions or milestones that should trigger emails). Some examples:
- After expressing interest (e.i, filling out a form): Send related content or a comparison guide
- After signup: Send a welcome series introducing your brand and value.
- After the first purchase: Trigger onboarding or how-to emails
- After inactivity: Send re-engagement nudges or win-back offers
- Segment email lists by journey stage: Use the journey map to segment based on where users currently are.
- Repurpose journey insights into email content themes: The questions, objections, and motivations you identify in your journey map can become rich insights for personalizing your email content.
For example, if your pricing appears to be a conversion blocker, you might send an email featuring an ROI calculator or a persuasive case study. If they feel overwhelmed, offer a straightforward starter guide to simplify their next step.
Or, after completing a trial, prompt them with success stories to encourage an upgrade. - Test, measure and iterate by stage: Track email performance by journey stage instead of as one-size-fits-all. Here are some examples:
- Awareness: Signup rates, CTR on lead magnets
- Consideration: Email opens, content engagement, replies
- Purchase: Click-through to checkout, coupon redemptions, active service usage
- Retention: Open rates on post-purchase series, repeat purchases
- Advocacy: Referral clicks, review submission rates
- Use the map to break the silos (Pro Tip):
Here, I need to give you a bit of background. Imagine a marketing team throwing MQLs over the wall and sales calling them “not warmed-up enough.” It happens, but it’s only a mundane interdepartmental blame game, especially in B2B.
This is what marketers and LinkedIn gurus call ‘working in silos’ – a disconnected way of working where every department lives in their bubble, chasing individual KPIs without understanding that the metric that truly matters is the revenue.
In the context of email marketing, you can prevent this with an email strategy that is not just transparent to, but also closely aligned with your sales, product, and support teams to ensure a cohesive customer experience. Admittedly, this is harder said than done, but far from impossible.
Email marketing customer journey examples
To ensure you get the right picture of the email marketing customer journey and its role, it pays to check some examples:
1. Sephora – Beauty insider tiered-loyalty emails
Sephora’s Beauty Insider program keeps email touchpoints tightly aligned with its three spending tiers (Insider, VIB, Rouge).
For retention, members who are getting close to an upgrade receive a real-time progress note (e.g., “You’re 120 points from Rouge”) showing their exact balance, a countdown bar, and a “double-points weekend” nudge.
In the advocacy phase, the annual birthday email lets VIB and Rouge members swap their gift for an extra 250 points, reinforcing the “spend-for-status” habit.
Sephora backs these emails with a live points feed and tier-specific CTAs so members can convert curiosity into a purchase in one click.
The result?
25 million + members worldwide!
2. Headspace – Email marketing and meditation journeys come together
The Headspace example is quite an esoteric, albeit fun way to explain the concept of email marketing customer journey.
The service eases new users into meditation with a four-email journey that mirrors the path from first curiosity to daily habit.
The Awareness email “Welcome to Headspace” uses plenty of white space, a single calming GIF, and one CTA that launches a one-minute breathing exercise.
Next, the Consideration email, “Science of Meditation,” backs the practice with peer-reviewed results and links to an expert video.
Early Retention kicks in a few days later with “Streak Builder,” where a gamified progress bar shows completed sessions and the next milestone, nudging commitment.
Finally, the Retention email, “Your 30-Day Challenge,” invites subscribers to a guided month-long plan while enabling push-notification reminders to keep momentum.
How to create an email marketing customer journey map
Follow the steps below to create customer journey maps to support your email marketing strategy.
- Define your personas (Who): Identify your main customer segments. Gather data (age, interests, pain points) and craft buyer personas. Understanding these personas ensures your emails will speak to real needs.
- Outline stages (When and Where): Choose the stages of your funnel (common ones: Awareness, Consideration, Decision/Purchase, Retention, Advocacy). Write what a potential customer does and feels at each stage.
- List email touchpoints: List all email triggers and campaigns you have or need for each stage. For examples:
- Newsletter signup (Awareness)
- Welcome series (Awareness/Consideration)
- Cart abandonment (Decision)
- Purchase receipt (Purchase)
- Onboarding tips (Retention)
- Re-engagement campaigns (Retention)
- Referral requests (Advocacy)
Tip: Don’t forget transactional emails (password reset, shipping confirmations, invoice emails, etc.) as a part of the journey.
- Create the map: Design a diagram (or spreadsheet) with stages on one axis and desired actions on the other.
- Analyze data (Why): Use your analytics to see how customers move. Check your sales pipeline, web analytics, and campaign results. Ask: Where do most people drop off? Do people often abandon carts? Do they engage with newsletters?
Look at actual purchasing paths and how customers behave at each touchpoint. Also, examine pain points from support or reviews. - Identify gaps and opportunities: With the map and data, inspect if there are missing messages at specific touchpoints or weak spots. For example, do you have a follow-up after a download? Or if there’s a lull of silence after a purchase? Fill those gaps. The journey map highlights where a helpful nudge is needed.
- Assign content and tone: For each email on your map, define its goal and message (see next section). Decide on tone, CTA, and offer. For example, an abandoned-cart email offers a discount with a friendly reminder, while a birthday email is celebratory and personal.
- Validate with the team: Involve marketing, sales, and support teams. Share the map and refine it. Everyone should know their role at each stage (marketing handles awareness, support handles retention issues, etc.).
- Document and visualize: Put the final map into a shareable format (diagram, slide deck, or documented flow). A clear visual helps the whole team follow the plan.
- Iterate: The first map is a draft. After implementing some campaigns, revisit the map with real campaign data and feedback. The goal is continuous improvement.
In short, journey mapping answers four key questions:
- Who is doing what?
- When do they do it?
- Where do your recipients see you?
- How do you engage with the recipients?
How to design email marketing campaigns for a customer journey
Once you have your email marketing customer journey map, you can design each campaign to fit its stage. Here’s how:
- Awareness stage (top of funnel): The language of your emails at this stage should be informative, authoritative, yet friendly (you don’t want to scare your prospects away with heavy jargon).
Start by introducing your brand and benefits. Common emails at this stage include a welcome or thank-you for signing up, newsletter opt-in confirmation, or content offers (guides, blog updates).
Also, use mild CTAs like “Learn More” or “Join Us” and focus on engagement over immediate sales. For instance, a welcome email with a free tip builds interest.
It’s just the start, so keep it light and accessible.
- Consideration stage: The tone here should become more supportive and educational. It is the point when prospects are evaluating you versus your competitors, so send testimonials, case studies, or product demos.
Use dynamic personalization like recommendations based on past browsing.
CTAs can get stronger now but still soft: “Watch Demo,” “See How It Works,” or a “Free Trial” sign-up.
If a lead has abandoned a cart, send a friendly reminder with an incentive, such as “Complete your order now with 10% off.”
- Decision/purchase stage: Here, your customer is almost ready to buy, so emails should be reassuring and action-oriented (action as in conversion).
You can improve your conversion rates by using age-old marketing tactics like creating a sense of urgency (limited offers), the bundling effect, or simply the thrill of grabbing a discount.
Plus, it should be stupid-simple to complete the purchase. Common campaigns at this stage include final nudges for abandoned carts, coupon or promo emails, and free shipping alerts.
Also, after a sale, follow up immediately with transactional emails like order confirmations, shipping info, and a thank-you.
You can also share a ‘next purchase’ incentive at this point. Only make sure not to cram too many things into one email. For instance you can send the order confirmation or shipping info with a thank-you note, then the ‘next purchase’ incentive as a follow-up.
- Retention stage: After a sale, it’s time you shift to value-driven messaging. Send tutorials, usage tips, or care instructions to help users enjoy the product (e.g., how-to guides or product maintenance tips).
Also, send personalized recommendations based on their purchase history. Loyalty rewards programs or “exclusive member” emails fit quite well here. The tone here should be appreciative and helpful (reward them for being customers and create a sense of belonging).
- Advocacy stage: This is the last stage where the fans of your product/service become your brand advocates. So, for them to be able to promote your venture, emails should make it easy to review or share it.
Here’s a table with a list of email types and their respective journey stage for quick reference:
| Email Type | Purpose & Details | Stage in Journey |
| Welcome Series | Triggered on sign-ups; uses 2–3 emails to introduce the brand and set expectations. | Awareness / Consideration |
| Educational Nurture Emails | Sent to engaged leads, the emails should share blog posts, e-books, or webinars related to their interests to build trust and authority (good for mid-funnel). | Consideration |
| Product/Service Updates | Shares news about new features or releases; helpful during the consideration or retention stages. | Consideration / Retention |
| Promotional/Coupons | Provides discounts or specials; useful around decision time or for re-engaging lapsing customers. | Decision / Re-engagement |
| Abandoned Cart Emails | Triggered when someone adds items to the cart but leaves without buying; usually involves a reminder and follow-up with incentives to recover lost sales. | Decision |
| Transactional Emails | Include order confirmations, shipping updates, receipts, and essential emails with near 100% open rates, belonging to the purchase stage. | Purchase |
| Onboarding Emails | Sent to new users or trial participants, step-by-step guides help customers get started and stay engaged. | Retention |
| Re-Engagement Emails | Sent to inactive subscribers; typically include a “We Miss You” message or exclusive offer to encourage reactivation. | Retention / Re-engagement |
| Feedback/Survey Emails | Sent after key actions (e.g., purchases, course completions) to gather feedback or reviews; used to improve services and build advocacy. | Retention / Advocacy |
Marketing automation and sequencing
To further enhance your email marketing efficiency, you can automate email sequences using tools like Mailtrap, Mailchimp, HubSpot, ActiveCampaign, etc.
These tools let you set up triggers (e.g., “when a user signs up” or “30 days after last purchase”) and automatically send the right email.
Let me show you some email marketing automations that most businesses deploy:
- A welcome automation: Instantly send a welcome email, then a follow-up after a day or two with more info or an offer.
- An abandoned cart flow: Send an email a few hours after cart abandonment, then a reminder with a coupon.
- A win-back series: If a customer hasn’t opened emails in 60 days, send a “We miss you” email with a special deal.
Automation saves time and keeps the journey consistent without manual effort. It also makes it easy to personalize as you can insert the customer’s name, mention past purchases, or adapt content blocks based on their interests.
Setting goals and KPIs
To get the most out of the email marketing customer journey, you must also know how to measure its performance.
So here’s a stage-level breakdown of what goals and metrics you must track:
| Journey Stage | KPIs to Watch |
| Awareness/Lead | Subscription rate (percentage of site visitors who sign up), click-through rate, and conversions from ad emails to signup. |
| Consideration | Email open rates (healthy range typically 20–30%, industry-dependent); click-through rates (CTR); landing page actions like demo requests. |
| Decision/Purchase | Email-driven sales and conversion rates (percentage of clicks leading to purchase); cart recovery rates from abandoned cart emails. |
| Retention | Repeat purchase rate and customer lifetime value driven by email offers; redemption rate of rewards or promo codes from loyalty emails. Or, in the SaaS space, it could be upgrades to a higher tier. |
| Advocacy | Number of referrals generated; number of reviews submitted through emails. |
Important: In addition to the KPIs mentioned above related to different journey stages, some KPIs must be tracked throughout the campaign. These include unsubscribe rates, bounce rates, and spam complaints.
Email marketing customer journey mapping software
We’ve talked about how to create an email marketing customer journey map, but you don’t have to draw it on paper. There are dedicated software solutions that take care of that.
Key features to look for in mapping software
Here’s a list of features to look for in a journey mapping software:
- Drag-and-drop email and journey builder
- Segmentation and personalization (dynamic content, condition splits)
- Analytics and reporting (open/click rates, conversion tracking)
- Templates and a responsive design editor
Top email marketing customer journey mapping software
Let’s look at some superior mapping software platforms:
1. Spreadsheets
A simple spreadsheet works great for an email journey map. You can create columns like Persona, Stage, Trigger, Email, KPI, etc.; add one row per touchpoint (e.g., “Signup → Welcome #1”).
Then you can colour-code stages, filter by persona, and drop in formulas to pull open-rate or revenue exports from your ESP. With Google Sheets or Excel, you get instant version control, easy sharing, and zero extra software to learn.
Note that this method requires some programming skills, so you can use Apps Script to create spreadsheet formulas to extract and manage the sheet’s data.
2. Native solutions in macOS
If you’re on a Mac, Freeform turns journey mapping into a visual drag-and-drop board.
Drop sticky notes for each stage (Awareness, Consideration, etc.), use shapes for triggers, and draw connectors to show flow.
You can also paste email mock-up screenshots, tag each note with a color per persona, and add quick comments for KPIs.
Because Freeform syncs over iCloud, teammates on macOS or iPadOS can edit live—no file-sharing gymnastics. It’s a zero-cost, native way to keep your email marketing funnel map transparent and collaborative.
3. FigJam
FigJam offers a structured “Journey Map” template where you can label columns for Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Retention, and Advocacy.
You can add sticky notes for each email trigger, annotate them with KPIs, and link supporting assets such as email mock-ups.
Also, team members can comment, tag owners, and view changes in real time; all edits save automatically in Figma’s cloud workspace.
4. Miro
Miro supplies a ready-made Customer Journey Map board with lanes for each funnel stage.
You can drag cards for triggers, assign colors for personas, and embed live data widgets from Google Sheets to monitor open and conversion rates.
The canvas in Miro supports task ownership fields, comment threads, and integrations with tools like HubSpot and Slack, so marketing, sales, and support can update the map and track progress in one place.
6. Mailchimp
Mailchimp is known for its intuitive interface. It provides a free plan for up to 500 contacts and 1,000 emails per month. The “Customer Journeys” is an automation feature that allows you to create visual email flows. Paid plans offer advanced automations and multivariate testing.
7. ActiveCampaign
ActiveCampaign offers powerful automation and a built-in CRM. While there’s no free tier, a 14-day free trial is available. The Lite plan starts at approximately $29/month for 500 contacts, providing unlimited emails and advanced personalization features.
8. HubSpot Marketing Hub
HubSpot includes email and automation tools with a free CRM that allows up to 2,000 emails per month. Paid plans add workflow automations and branching journeys, suitable for scaling businesses.
9. Ortto (formerly Autopilot)
Ortto is a visual journey builder focused on mid-market teams. It offers a 14-day free trial, with professional plans starting around $509/month for up to 10,000 contacts. Features include a drag-and-drop journey builder, email/SMS capabilities, pop-ups, and analytics.
Other notable software: MailerLite, Moosend, Klaviyo (eCommerce-focused), Customer.io, etc.
How to track and optimize the customer journey using email marketing analytics
Once your customer journey is set up and running, it’s time to measure everything and keep tweaking to maximize your time and budget.
Use these tactics and metrics:
Important email metrics you must track
You should regularly check how your emails are performing. Look at things like:
- How many emails were delivered (95% + of your emails should be delivered)
- How many bounced back (bounces should be lower than 2%)
- If anyone marked them as spam (the rate should be lower than 0.1%)
- How many people opened your emails (averages between 15% and 25%, with some industries citing up to 35%)
- How many clicked on links inside them (the average across different industries is about 2.7%, and the good click rate is between 2% and 5%)
- How many opened and clicked (click-to-open rate) (it’s tricky to provide averages since different sources provide quite a different range, going as low as ~5% or as high as ~30%)
- How many unsubscribed (the average is 0.26% across different industries)
Also, track your conversion rate. It tells you how many people took action (like made a purchase or signed up). If you see lots of bounces or spam complaints, your email list might need cleaning.
Open and click rates show if people are interested, and show whether your emails are driving real results.
Test what works (A/B testing)
Try small changes to see what gets better results. You can A/B test subject lines, sender names, button text, images, or send times.
Even tiny changes can boost open or click rates. Most email tools make it easy to run these tests and show you what works best.
Get personal with segments
A survey by Venturebeat.com reported that about 20% of marketers observed a 15-20% increase in email open rates when they invested efforts in personalization:
And only 5% of marketers reported no increase in open rates from personalization.
I’m guessing your business doesn’t fall under those 5%, so you must use what you know about your customers to send more relevant emails.
For example, if you’re a SaaS, you can customize content based on someone’s location, purchase behaviour, industry, or feature usage.
Sure, there are a bunch of other ways to do it, but however you approach personalization, double down on your efforts to handle user data safely.
Track your email flows
If you’re using automation, check how each part of your flow is doing.
For example, how many people start your welcome series? How many finish it? If one email has low opens, try changing the subject line or send time.
It also pays to run a technical inspection of the entire automation flow every now and again to ensure all triggers and actions work properly, without blocks and data bottlenecks.
Ask for feedback
Feedback helps you improve. Send short surveys after someone buys something. Ask new subscribers what kind of emails they want.
If someone stops opening your emails, ask why, ou can fix a lot of issues just by listening.
Use Google Analytics and your CRM
Google Analytics helps you track the source of your website traffic.
For instance, it can track visitors from affiliate links, social media posts, paid ads, etc.
And yes, Email’s part of the list too (you can check all the sources tracked by GA4 here).
You just need to add UTM tracking links (e.g., utm_source=newsletter, utm_medium=email) to your emails, and Google Analytics will be able to tell you that the site visitor came from an email.
Also, if your email tool connects with your CRM (like HubSpot or Salesforce), you can track who becomes a customer and what emails helped get them there.
Keep improving
Your email journey should never be on autopilot. Review your numbers often.
- If open rates drop, try new subject lines or send to smaller, more targeted groups.
- If people aren’t clicking, try stronger call-to-action buttons.
The key is to test, learn, and improve constantly.
Wrapping up
We covered a lot about the email marketing customer journey, from mapping each stage to crafting emails that truly address customer needs. It’s clear that understanding your customer’s path is critical for effective communication, be it emails or even some other medium.
Now, if you’re looking for a tool to bring all this into action, consider Mailtrap. It’s designed to help you create, test, and send emails that align perfectly with your customers’ journey. With features like a drag-and-drop editor, pre-designed templates, and detailed analytics, Mailtrap simplifies the process.
Whether you’re just starting or looking to refine your strategy, Mailtrap offers a free plan to get you going. It’s user-friendly and built to support your growth every step of the way.
Ready to enhance your email marketing?
Try Mailtrap for free.